BIM Use: Digital Fabrication
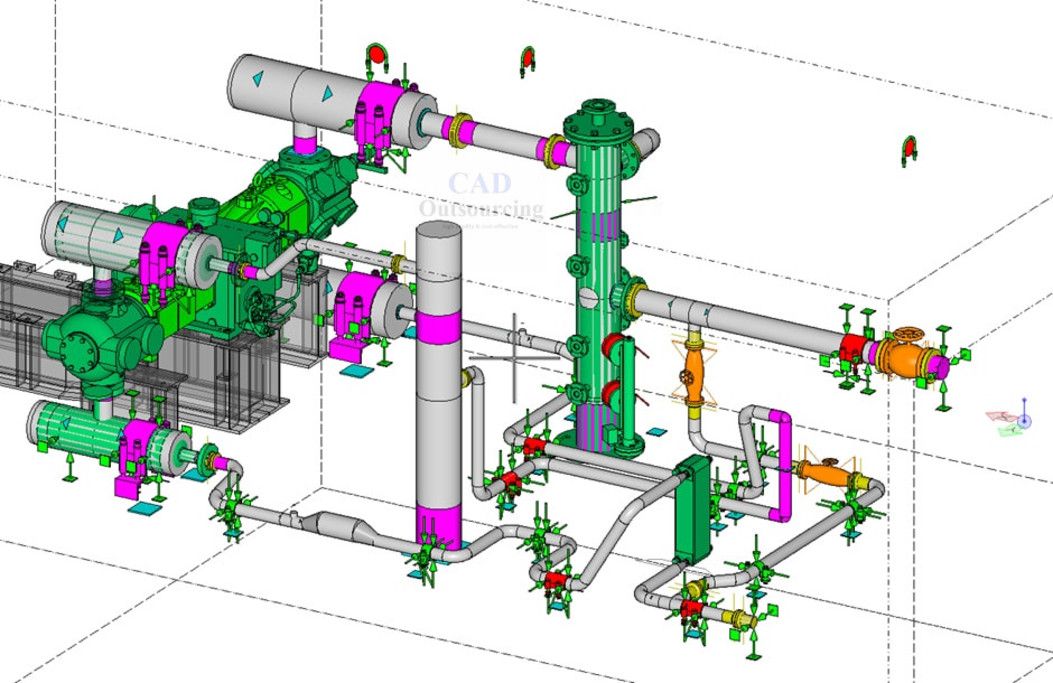 Digital Fabrication
Digital Fabrication
A process that uses digitized information to facilitate the fabrication of construction materials or assemblies directly from the 3D model.
Common uses include sheet metal fabrication, structural steel cutting, pipe spooling, and rapid prototyping. This process ensures that the downstream manufacturing phase has minimum ambiguities and sufficient information to fabricate with minimal waste.
| Potential Value: |
|---|
- Ensuring high quality of information (zero transcription errors).
- Minimize tolerances through precise machine fabrication.
- Increase fabrication productivity and safety.
- Reduce lead time by automating data transfer.
- Adapt late changes in design more efficiently.
- Reduced dependency on 2D paper drawings (shop drawings).
| Resources Required: |
|---|
- Design Authoring Software (e.g., Tekla, Revit with plugins)
- Machine-readable data formats (e.g., NC1, MAJ, DXF)
- Fabrication hardware (CNC machines, Laser cutters)
| Team Competencies: |
|---|
- Ability to create LOD 400 fabrication models.
- Ability to extract digital information for fabrication from 3D models.
- Understanding of CNC manufacturing limitations and protocols.
- Ability to manufacture building components using digital information.